TIBCO ComputeDB Cluster Architecture
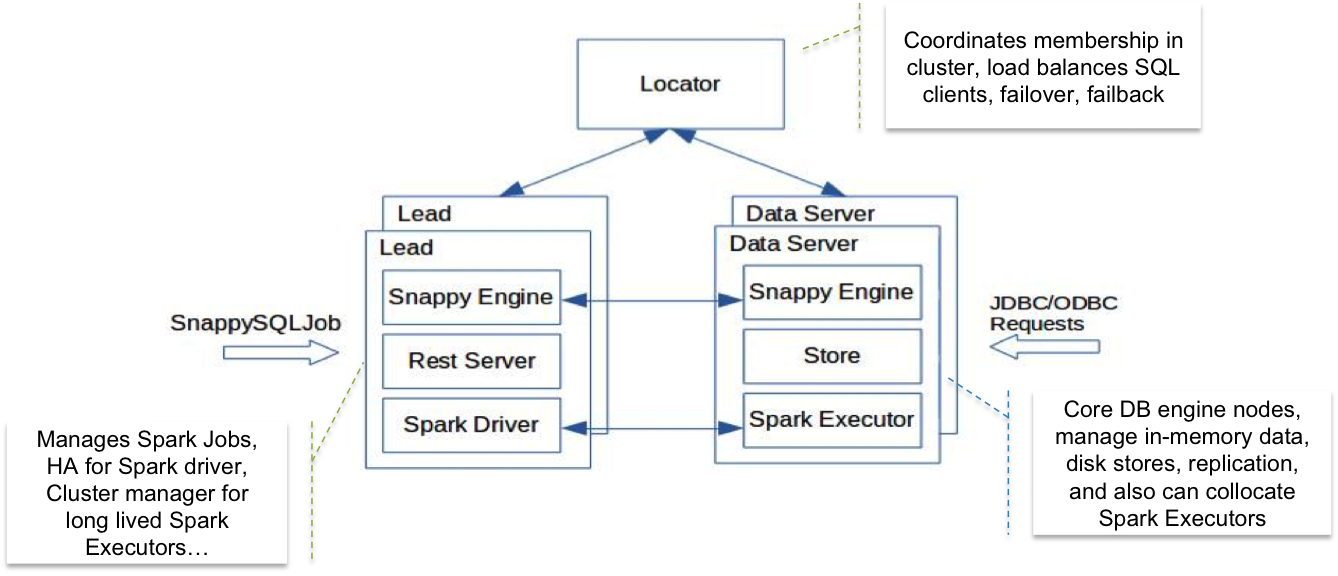
A TIBCO ComputeDB cluster is a peer-to-peer (P2P) network that comprises of three distinct types of members which are represented in the following figure:
-
Locator: Locator members provide discovery service for the cluster. They inform the new member joining the group about the other existing members. A cluster usually has more than one locator for high availability reasons.
-
Lead Node: The lead node member acts as a Spark driver by maintaining a singleton SparkContext. There is one primary lead node at any given instance but there can be multiple secondary lead node instances on standby for fault tolerance. The lead node hosts a REST server to accept and run applications. The lead node also executes SQL queries routed to it by “data server” members.
-
Data Servers: A data server member hosts the data, embeds a Spark executor, and also contains a SQL engine capable of executing certain queries independently and more efficiently than Spark. Data servers use intelligent query routing to either execute the query directly on the node or pass it to the lead node for execution by Spark SQL.
TIBCO ComputeDB also has multiple deployment options. For more information refer to, Deployment Options.
Interacting with TIBCO ComputeDB
Note
For the section on the Spark API, it is assumed that users have some familiarity with core Spark, Spark SQL, and Spark Streaming concepts. Moreover, you can try out the Spark Quick Start. All the commands and programs listed in the Spark guides work in TIBCO ComputeDB as well. For the section on SQL, no Spark knowledge is necessary.
Interfaces are provided for developers, familiar with Spark programming as well as SQL, to interact with TIBCO ComputeDB. JDBC can be used to connect to the TIBCO ComputeDB cluster and interact using SQL. On the other hand, users comfortable with the Spark programming paradigm can write jobs to interact with TIBCO ComputeDB. Jobs can be like a self-contained Spark application or can share the state with other jobs using the TIBCO ComputeDB store.
Unlike Apache Spark, which is primarily a computational engine, the TIBCO ComputeDB cluster holds mutable database state in its JVMs and requires all submitted Spark jobs/queries to share the same state (of course, with schema isolation and security as expected in a database). This required extending Spark in two fundamental ways.
-
Long running executors: Executors are running within the TIBCO ComputeDB store JVMs and form a p2p cluster. Unlike Spark, the application Job is decoupled from the executors - submission of a job does not trigger the launching of new executors.
-
Driver runs in HA configuration: The Spark driver manages the assignment of tasks to these executors. When a driver fails, this can result in the executors getting shut down, taking down all cached state with it. Instead, TIBCO ComputeDB leverages the Spark JobServer to manage Jobs and queries within a "lead" node. Multiple such leads can be started and provide HA (they automatically participate in the TIBCO ComputeDB cluster enabling HA).
In this document, mostly the same set of features via the Spark API or using SQL is showcased. If you are familiar with Scala and understand Spark concepts you can choose to skip the SQL part go directly to the Spark API section.
High Concurrency in TIBCO ComputeDB
Thousands of concurrent ODBC and JDBC clients can simultaneously connect to a TIBCO ComputeDB cluster. To support this degree of concurrency, TIBCO ComputeDB categorizes incoming requests from these clients into low latency requests and high latency ones.
For low latency operations, Spark’s scheduling mechanism is completely bypassed and directly operate on the data. High latency operations (for example, compute-intensive queries) are routed through Spark’s fair scheduling mechanism. This makes TIBCO ComputeDB a responsive system, capable of handling multiple low latency short operations as well as complex queries that iterate over large datasets simultaneously.
State Sharing in TIBCO ComputeDB
A TIBCO ComputeDB cluster is designed to be a long-running clustered database. The state is managed in tables that can be shared across any number of connecting applications. Data is stored in memory and replicated to at least one other node in the system. Data can be persisted to disk in shared nothing disk files for quick recovery. Nodes in the cluster stay up for a long time and their lifecycle is independent of application lifetimes. TIBCO ComputeDB achieves this goal by decoupling its process startup and shutdown mechanisms from those used by Spark.